学习笔记
交互式是不创建脚本文件,通过解释器的交互模式来编写代码
在 Python 里,标识符由字母、数字、下划线 组成。
在 Python 中,所有标识符可以包括英文、数字以及下划线(_),但不能以数字开头。
Python 中的标识符是区分大小写 的。
以下划线开头的标识符是有特殊意义的。以单下划线开头 _foo 的代表不能直接访问的类属性,需通过类提供的接口进行访问,不能用 from xxx import * 而导入。
Python 可以同一行显示多条语句,方法是用分号 ;
运算符
描述
[] [:]下标,切片
**指数
~ + -按位取反, 正负号
* / % //乘,除,模,整除
+ -加,减
>> <<右移,左移
&按位与
^ |按位异或,按位或
<= < > >=小于等于,小于,大于,大于等于
== !=等于,不等于
is is not身份运算符
in not in成员运算符
not or and逻辑运算符
= += -= *= /= %= //= **= &= `= ^=` `>>=` `<<=`
and
exec
not
assert
finally
or
break for pass
class from
print
continue
global
raise
def
if return
del
import try
elif in while
else is with
except
lambda
yield
python可以写任意大 的整数
如果出现很大的数比如说10000000可以写成10000_000
浮点数可以用科学计数法来表示
1 2 round(11.111,2)这个函数是四舍五入round(x[,d])d为保留位数默认为0 // 11.11
1 2 3 4 pow(x,y[,z]) 幂余 pow(2,3,3) //2
字符串是以单引号或者双引号写出来的
字符串内部中有"或者‘可以通过\来表示
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 'I\'m \"OK\"!' I'm "OK"! str1 = ' hello, world!' # 通过内置函数len计算字符串的长度 print(len(str1)) # 13 # 获得字符串首字母大写的拷贝 print(str1.capitalize()) # Hello, world! # 获得字符串每个单词首字母大写的拷贝 print(str1.title()) # Hello, World! # 获得字符串变大写后的拷贝 print(str1.upper()) # HELLO, WORLD! # 从字符串中查找子串所在位置 print(str1.find(' or')) # 8 print(str1.find(' shit')) # -1 # 与find类似但找不到子串时会引发异常 # print(str1.index(' or')) # print(str1.index(' shit')) # 检查字符串是否以指定的字符串开头 print(str1.startswith(' He')) # False print(str1.startswith(' hel')) # True # 检查字符串是否以指定的字符串结尾 print(str1.endswith(' !')) # True # 将字符串以指定的宽度居中并在两侧填充指定的字符 print(str1.center(50, ' *')) # 将字符串以指定的宽度靠右放置左侧填充指定的字符 print(str1.rjust(50, ' ')) str2 = ' abc123456' # 检查字符串是否由数字构成 print(str2.isdigit()) # False # 检查字符串是否以字母构成 print(str2.isalpha()) # False # 检查字符串是否以数字和字母构成 print(str2.isalnum()) # True str3 = ' jackfrued@126. com ' print(str3) # 获得字符串修剪左右两侧空格之后的拷贝 print(str3.strip())
字符串函数
返回从左边第一个指定的字符索引,找不到返回-1
返回从左边第一个字符索引,找不到报错
1 2 3 4 5 6 str = "abcde" print (str .find('c' ))//2 str = "hello world" a = str .index('w' ) print (a)//6
字符串的拆分
1 2 str = "hello world" print (str .split(' ' ))//['hello' , 'world' ]
方法必须用.方式
八种重要字符串的方法
str.lower str.upper() 返回字符串的副本,全部为大小写
str.split(sep=None)返回一个列表,由str根据sep被分割的部分组成
str.count(sub)返回子串sub在str中中出现个数
python用于槽方式以及format方式
1 "{}是世界上最好用的语言之一,而{}是效率最高的语言".format("python","c++")
只有两个True和False
布尔值可以tong过and or not表达
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 >>> True and False False >>> False and False False >>> 5 > 3 and 3 > 1 True >>> True or True True >>> True or False True >>> not False True
用None表示,不能单纯理解为0
重点
python解释器干了两个事情
在内存中创建了‘abc’的字符串
在内存中创建a的变量指向‘abc’
list是一种有序的集合,可以进行修改或者删除
1 classmates=['song' ,'wang' ,'zhang' ]
使用len可获取list元素的个数
用索引可以访问list的元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 >>> classmates[0 ]'song' >>> classmates[1 ]'wang' >>> classmates[2 ]'zhang' >>> classmates[3 ]Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>" , line 1 , in <module> IndexError: list index out of range list1 = [1 , 3 , 5 , 7 , 100 ] print (list1) list2 = ['hello' ] * 3 print (list2) print (len (list1)) print (list1[0 ]) print (list1[4 ]) print (list1[-1 ]) print (list1[-3 ]) list1[2 ] = 300 print (list1) for index in range (len (list1)): print (list1[index]) for elem in list1: print (elem) for index, elem in enumerate (list1): print (index, elem)
当然我们也可以通过负数来索引
1 2 >>> classmates[-1 ]'zhang'
因为list为可变的有序表 append
1 2 3 >>> classmates.append('zhao' )>>> classmatesclassmates=['song' ,'wang' ,'zhang' ,'zhao' ]
元素想插入到指定的位置中.insert
1 2 3 4 5 >>> classmates.insert(1 , 'Jack' )>>> classmates>>> classmates.append('zhao' )classmates=['song' ,'jack' ,'wang' ,'zhang' ,'zhao' ]
删除末尾用 pop()
1 2 3 4 >>> classmates.pop()'zhao' >>> classmates['song' ,'jack' ,'wang' ,'zhang' ]
想删除指定的位置用pop(i)
1 2 3 4 >>> classmates.pop(1 )'Jack' >>> classmates['Michael' , 'Bob' , 'Tracy' ]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 list1 = [1 , 3 , 5 , 7 , 100 ] list1.append(200 ) list1.insert(1 , 400 ) list1 += [1000 , 2000 ] print (list1) print (len (list1)) if 3 in list1: list1.remove(3 ) if 1234 in list1: list1.remove(1234 ) print (list1) list1.pop(0 ) list1.pop(len (list1) - 1 ) print (list1) list1.clear() print (list1)
1 2 3 4 f = [x for x in range (1 , 10 )] print (f)f = [x + y for x in 'ABCDE' for y in '1234567' ] print (f)
list中可以有不同类型的甚至list
1 2 3 >>> s = [22141 , True , ['asp' , 'php' ], 'scheme' ]>>> len (s)4
有序的列表叫tuple,tuple不能被修改
不可变的tuple有什么意义?因为tuple不可变,所以代码更安全。如果可能,能用tuple代替list就尽量用tuple。
1 2 3 >>> t = (1 , 2 )>>> t(1 , 2 )
如果tuple中出现list也是可以修改的
1 2 3 4 5 >>> t = ('a' , 'b' , ['A' , 'B' ])>>> t[2 ][0 ] = 'X' >>> t[2 ][1 ] = 'Y' >>> t('a' , 'b' , ['X' , 'Y' ])
其他的语言叫map
使用key-value
dict实现,只需要一个“名字”-“成绩”的对照表,直接根据名字查找成绩,无论这个表有多大,查找速度都不会变慢。用Python写一个dict如下:
1 2 3 >>> d = {'Michael' : 95 , 'Bob' : 75 , 'Tracy' : 85 }>>> d['Michael' ]95
必须要有key才能读取value
如果想删除只要删除key就可以了
set和dict类型
是存放key的但是不存放value key不能重复
set具有数学上的set性质
比如无序,没有重复元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 >>> s = set ([1 , 2 , 3 ])>>> s{1 , 2 , 3 } >>> s.add(4 )>>> s{1 , 2 , 3 , 4 } >>> s.add(4 )>>> s{1 , 2 , 3 , 4 } >>> s.remove(4 )>>> s{1 , 2 , 3 }
和c语言基本相似
注意不要少写了冒号
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 age = 3 if age >= 18 : print ('your age is' , age) print ('adult' ) else : print ('your age is' , age) print ('teenager' )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 age = 3 if age >= 18 : print ('adult' ) elif age >= 6 : print ('teenager' ) else : print ('kid' ) if <条件判断1 >: <执行1 > elif <条件判断2 >: <执行2 > elif <条件判断3 >: <执行3 > else : <执行4 >
python中的循环分为for in依次将list或者tuple中元素迭代
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 names = ['Michael' , 'Bob' , 'Tracy' ] for name in names: print (name) // Michael Bob Tracy
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 print ("hello world" )print (88 * 88 - 55 )fp = open ('E:/编程/python/text.txt' , 'a+' ) print ('hello world' , file=fp)fp.close() a, b = 5 , 10 print (f'{a} * {b} = {a * b} ' )
在list或者tuple取元素
range函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 >>>list (range (0 , 30 , 5 )) [0 , 5 , 10 , 15 , 20 , 25 ] >>> list (range (0 , 10 , 2 ))[0 , 2 , 4 , 6 , 8 ] >>> list (range (0 , -10 , -1 ))[0 , -1 , -2 , -3 , -4 , -5 , -6 , -7 , -8 , -9 ] >>> list (range (5 ))[0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 list 中可以通过for 来切片>>> r = []>>> n = 3 >>> for i in range (n):... r.append(L[i])... >>> r['Michael' , 'Sarah' , 'Tracy' ]
python有更简单的方法实现切片操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 >>> L[0 :3 ]['Michael' , 'Sarah' , 'Tracy' ] >>> L[:3 ]['Michael' , 'Sarah' , 'Tracy' ] >>> L[1 :3 ]['Sarah' , 'Tracy' ] 如果0 -99 提取前十 >>> L=list (rang(100 ))>>> l[0 ,1 ,2. ...99 ] >>> l[:10 ]l [0 ,1 ,...9 ] 前十个,每两个取一个 l[:10 :2 ] l[::5 ]
在python中通过for循环遍历list或者tuple叫迭送
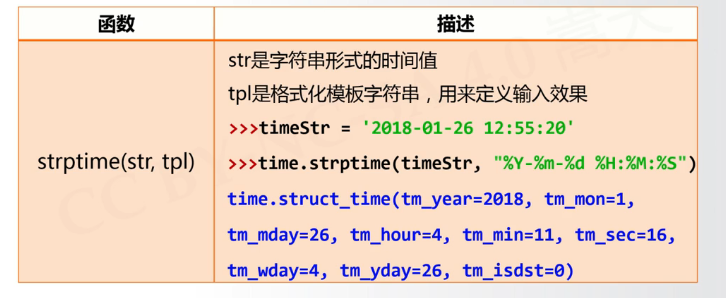
1 Wed Mar 23 21:57:29 2022
1 time.struct_time(tm_year=2022, tm_mon=3, tm_mday=23, tm_hour=13, tm_min=58, tm_sec=1, tm_wday=2, tm_yday=82, tm_isdst=0)
一年365进步与退步千分之一
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 def dayUp (df ): dayup = 1 for i in range (365 ): if i % 7 in [6 ,0 ]: dayup=dayup*(0.99 ) else : dayup =dayup*(1 +df) return dayup dayfactor = 0.01 while dayUp(dayfactor) < 37.78 : dayfactor+=0.001 print ("他工作日努力参数为{:.3f}" .format (dayfactor))//0.019
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import timescale = 10 print ("........执行开始........" )for i in range (scale+1 ): a='*' *i b = '.' *(scale-i) c = (i/scale)*100 print ("\r{:^3.0f}%[{}->{}]" .format (c,a,b)) time.sleep(0.1 ) print ("........结束........" )
…结束…")